Horse Nash, also known as equine odontoclastic tooth resorption and hypercementosis (EOTRH), is a painful dental condition that affects the teeth of older horses. This degenerative disease primarily targets the incisor teeth, but can also affect the cheek teeth in severe cases. While the exact causes of horse nash remain unclear, early detection and proper management are crucial to alleviate pain and improve your horse’s quality of life.
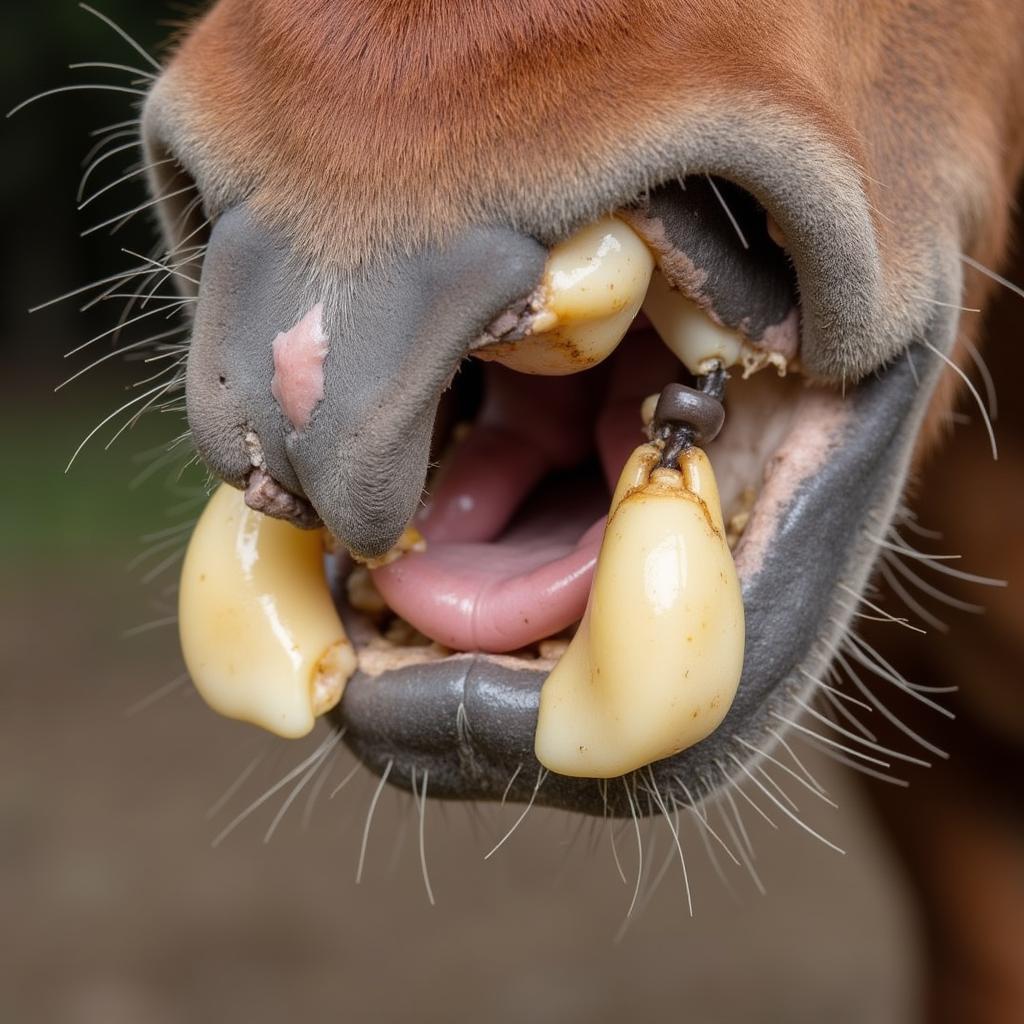 Close-up of horse incisors showing signs of nash
Close-up of horse incisors showing signs of nash
What Causes Horse Nash?
While research is ongoing, the exact cause of horse nash is still unknown. However, several factors are suspected to play a role in its development, including:
- Genetics: Some breeds, such as Thoroughbreds and Warmbloods, appear to be more predisposed to horse nash than others.
- Autoimmune Disorders: There is evidence to suggest that EOTRH might be linked to an autoimmune response, where the horse’s immune system mistakenly attacks the cells responsible for maintaining dental health.
- Dietary Factors: Imbalances in mineral intake, particularly calcium and phosphorus, could potentially contribute to tooth weakening and susceptibility to nash.
- Hormonal Influences: Age-related hormonal changes, particularly in older horses, are believed to potentially influence the development of EOTRH.
Recognizing the Signs of Horse Nash
Early detection of horse nash is essential for effective management. Keep a watchful eye out for these common symptoms, especially in horses over 15 years old:
- Difficulty Eating: You might notice your horse dropping feed, chewing slowly, or tilting its head while eating.
- Weight Loss: Struggling to chew properly can lead to inadequate food intake and subsequent weight loss.
- Excessive Drooling: Increased salivation is often a sign of oral discomfort and difficulty swallowing.
- Swollen Gums: Inflammation and swelling around the gums, especially near the affected teeth, are common.
- Loose or Missing Teeth: As nash progresses, the affected teeth may become loose and eventually fall out.
- Nasal Discharge or Facial Swelling: In severe cases, horse nash can lead to secondary infections, potentially causing nasal discharge or facial swelling.
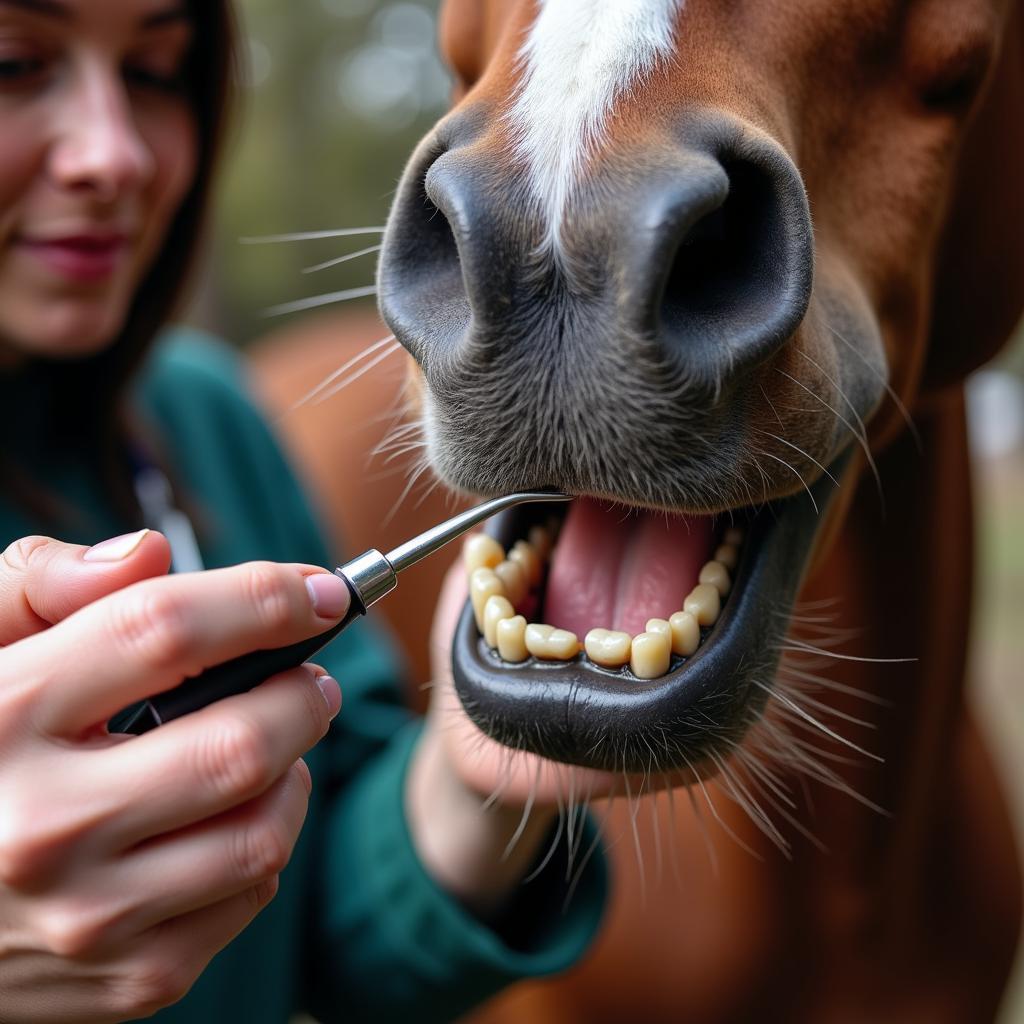 Veterinarian conducting a dental exam on a horse
Veterinarian conducting a dental exam on a horse
“Early diagnosis is key,” says Dr. Emily Carter, DVM, an equine dental specialist. “The sooner we can identify and manage horse nash, the better we can control the pain and slow the progression of the disease.”
Diagnosis and Treatment Options
A definitive diagnosis of horse nash requires a thorough oral examination by a qualified equine veterinarian. They will assess the condition of your horse’s teeth and gums, and may recommend dental X-rays to evaluate the extent of the damage.
While there is no cure for horse nash, the focus of treatment is to manage the pain and slow down the progression of the disease. Treatment options may include:
- Pain Relief: Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are commonly prescribed to alleviate pain and reduce inflammation.
- Dental Extraction: In severe cases, where teeth are loose or causing significant pain, extraction may be necessary.
- Dietary Modifications: Switching to softer feeds, such as senior feeds or soaked hay, can make it easier for your horse to eat.
- Regular Dental Checkups: Routine dental examinations, at least once a year, are crucial for early detection and management of horse nash.
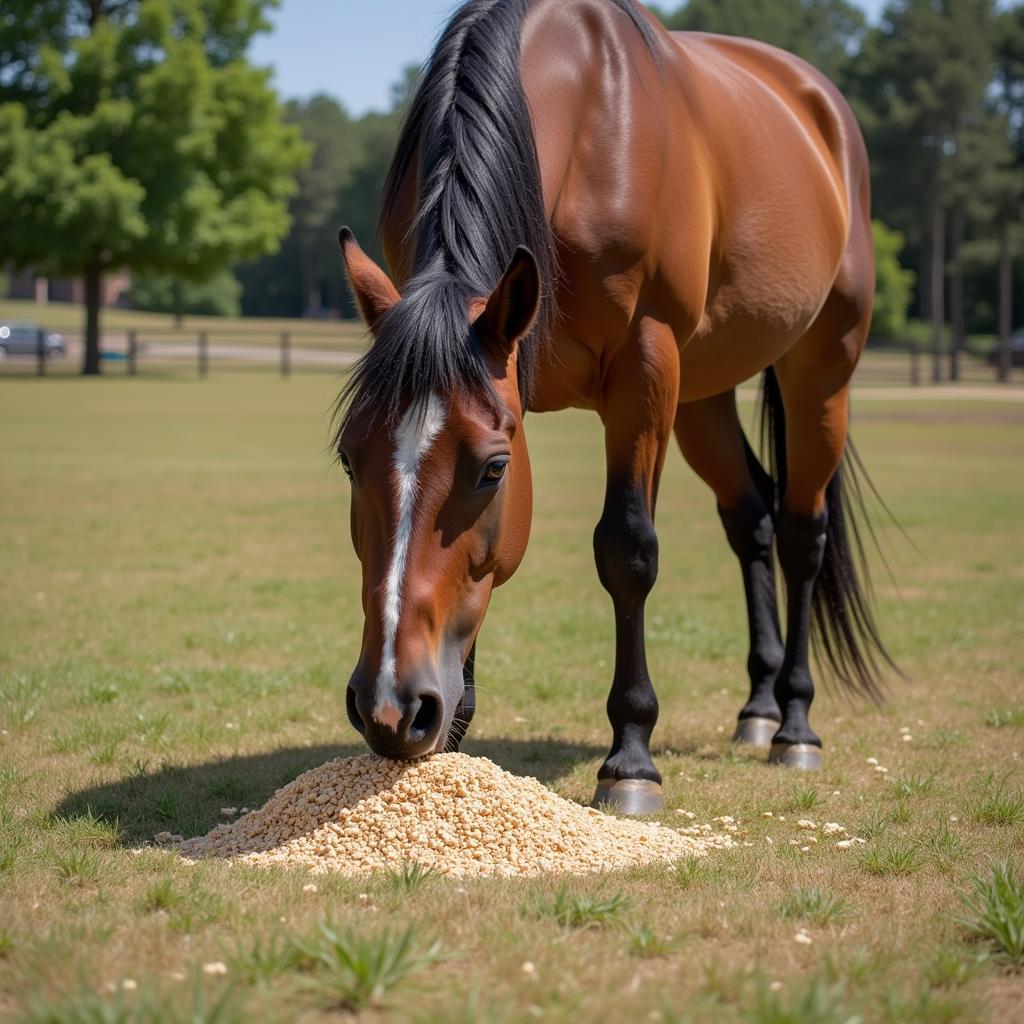 Horse comfortably eating senior feed from a bucket
Horse comfortably eating senior feed from a bucket
Living with Horse Nash: Tips for Owners
Caring for a horse with horse nash requires attentive management and adjustments to their routine. Here are some valuable tips:
- Monitor Your Horse Closely: Pay attention to their eating habits, weight, and any signs of discomfort.
- Provide a Comfortable Environment: Ensure your horse has access to soft bedding, fresh water, and a stress-free environment.
- Work Closely with Your Veterinarian: Regular checkups and open communication with your vet are crucial for effective management.
- Offer Support and Patience: Horses with horse nash may need extra time and patience when eating and being handled.
Conclusion
Horse nash is a challenging condition that can significantly impact a horse’s well-being. By understanding the causes, recognizing the symptoms, and providing appropriate care, horse owners can help their equine companions live more comfortably with this chronic disease. Regular veterinary checkups and attentive management are essential for early detection, pain relief, and promoting the best possible quality of life for horses affected by horse nash.
For personalized advice and support in managing your horse’s dental health, contact Justus Horses USA at 0772127271, email us at [email protected], or visit our facility located at QGM2+WX2, Vị Trung, Vị Thuỷ, Hậu Giang, Việt Nam. Our team of equine experts is available 24/7 to answer your questions and provide exceptional care for your cherished companions.