Tendinitis in horses, a common ailment affecting their leg tendons, can significantly impact their performance and well-being. This comprehensive guide will delve into the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment of tendinitis, equipping you with the knowledge to ensure your equine companion receives the best possible care.
What is Equine Tendinitis?
Tendinitis refers to the inflammation or damage of a tendon, the tough, fibrous tissue that connects muscle to bone. In horses, this condition most commonly affects the superficial digital flexor tendon (SDFT) and the deep digital flexor tendon (DDFT) in the lower leg, although other tendons can also be involved. Several factors can contribute to tendinitis, including overuse, improper training techniques, poor conformation, and trauma.
Understanding the underlying causes of tendinitis is crucial for effective prevention and treatment. Overexertion, especially on hard or uneven surfaces, can strain the tendons beyond their capacity, leading to microscopic tears and inflammation. Similarly, inadequate conditioning and sudden increases in workload can predispose horses to tendinitis. Conformation flaws can also place uneven stress on tendons, increasing the risk of injury.
The severity of tendinitis can range from mild strains to complete tendon ruptures. Early diagnosis and prompt treatment are essential to minimize long-term damage and promote healing.
You can find more information about treating tendon injuries on our horse tendon injury treatment page.
Recognizing the Signs of Tendinitis in Your Horse
Identifying tendinitis in its early stages is paramount to prevent further damage. Common signs include:
- Heat and swelling in the affected area
- Pain or lameness, especially after exercise
- Thickening or bowing of the tendon
- Reluctance to move or bear weight on the affected limb
If you notice any of these symptoms, it’s vital to consult a veterinarian for a proper diagnosis. Early intervention can significantly improve the prognosis and reduce the risk of long-term complications.
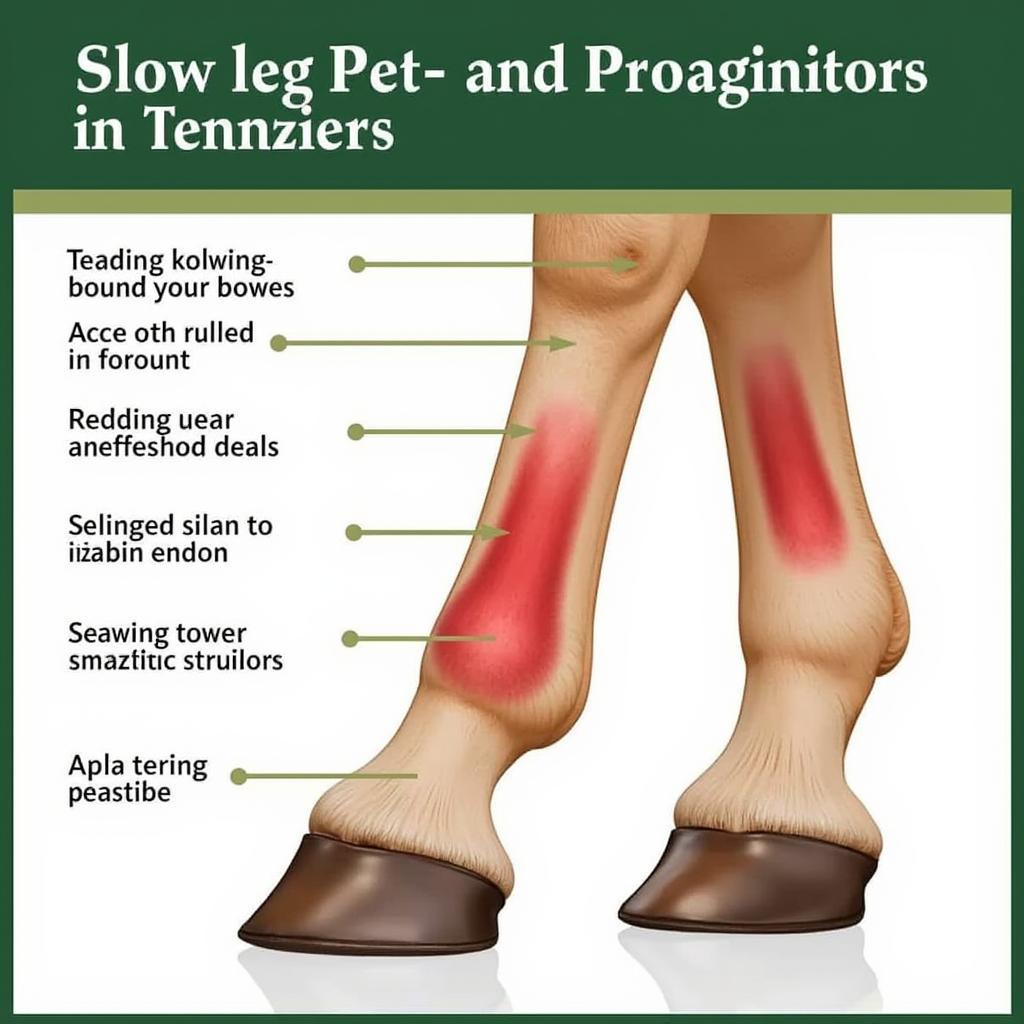 Inflammation in a Horse's Leg Due to Tendinitis
Inflammation in a Horse's Leg Due to Tendinitis
Diagnosing and Treating Tendinitis: A Comprehensive Approach
Veterinarians employ various diagnostic methods to confirm tendinitis, including physical examinations, ultrasound imaging, and sometimes, X-rays. Ultrasound is particularly valuable for assessing the extent of tendon damage and monitoring the healing process.
Treatment options for tendinitis vary depending on the severity of the condition. Conservative management often involves:
- Rest and restricted activity: Allowing the tendon time to heal is crucial.
- Cold therapy: Applying ice packs or cold hosing can help reduce inflammation. Learn more about effective methods for applying a poultice horse.
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs): These medications can help alleviate pain and inflammation.
- Controlled exercise: A gradual return to activity under veterinary guidance is essential. A horse leg brace may be necessary during rehabilitation.
In more severe cases, other therapies such as shock wave horse therapy, regenerative medicine, or surgery may be considered.
Dr. Emily Carter, DVM, a renowned equine veterinarian, emphasizes, “Early diagnosis and a multimodal treatment approach are key to successful tendinitis management. Ignoring the signs can lead to chronic lameness and significantly impact a horse’s athletic career.”
Preventing Tendinitis: Proactive Steps for Healthy Tendons
Preventing tendinitis is always preferable to treating it. Here are some proactive measures:
- Ensure proper conditioning: Gradually increase workload and avoid sudden changes in training intensity.
- Provide adequate warm-up and cool-down periods before and after exercise.
- Maintain good footing and avoid working on hard or uneven surfaces.
- Address conformation flaws through appropriate farriery and other corrective measures.
- Consider incorporating supportive therapies, such as Briotti Horse Chestnut, to maintain tendon health.
Dr. Sarah Miller, PhD, Equine Physiotherapist, advises, “Proper conditioning and management are essential for preventing tendinitis. Consistent exercise, balanced nutrition, and regular veterinary check-ups are crucial for maintaining healthy tendons.”
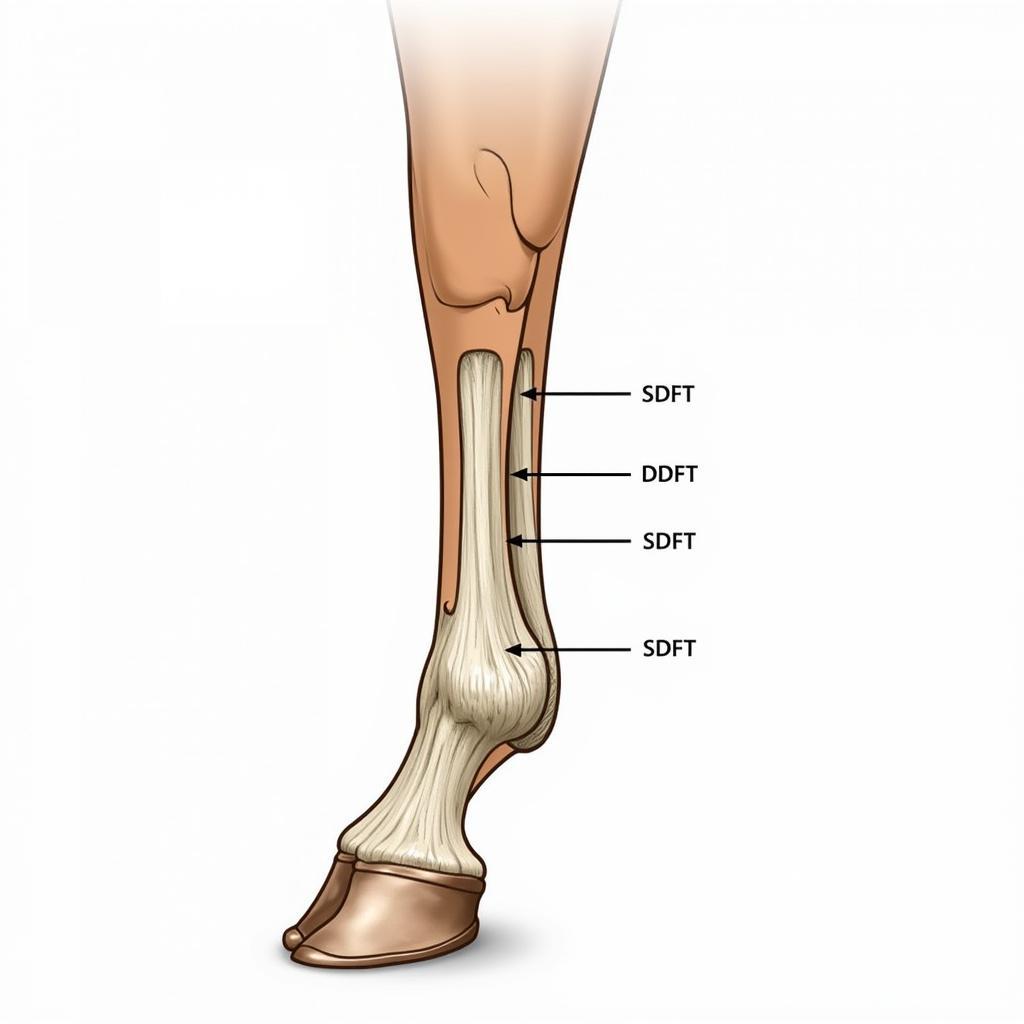 Horse Leg Anatomy Highlighting Tendons
Horse Leg Anatomy Highlighting Tendons
Conclusion
Tendinitis in horses is a serious condition that requires prompt attention. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options, you can play a vital role in ensuring your horse’s well-being. Early intervention and proactive management are essential for minimizing long-term damage and promoting a full recovery. Remember, a healthy horse is a happy horse!
FAQ
- What are the most common signs of tendinitis in horses? Heat, swelling, lameness, and thickening of the tendon.
- How is tendinitis diagnosed? Through physical exams, ultrasound, and sometimes X-rays.
- What are the treatment options for tendinitis? Rest, cold therapy, NSAIDs, controlled exercise, and in severe cases, shockwave therapy or surgery.
- Can tendinitis be prevented? Yes, through proper conditioning, good footing, and addressing conformation flaws.
- What is the prognosis for horses with tendinitis? It varies depending on the severity and promptness of treatment.
- When should I contact a veterinarian? If you notice any signs of lameness or discomfort in your horse’s legs.
- How long does it take for a horse to recover from tendinitis? It can take several months or even longer, depending on the severity.
Need More Help?
For further assistance and personalized advice, contact us:
Phone: 0772127271
Email: [email protected]
Address: QGM2+WX2, Vị Trung, Vị Thuỷ, Hậu Giang, Việt Nam
Our dedicated customer care team is available 24/7 to answer your questions and provide expert guidance. You can also explore other relevant articles on our website for more in-depth information on equine health and care.