The Fetlock On A Horse is a crucial joint, often compared to the ankle in humans. It plays a vital role in the horse’s movement and ability to absorb shock. Understanding its anatomy and function is essential for any horse owner or enthusiast. This article will delve into the intricacies of the fetlock, covering its structure, common injuries, and protective measures. For those interested in where the fetlock is located, check out our guide on where is a horse’s fetlock.
The Anatomy of a Horse’s Fetlock
The fetlock joint, also known as the metacarpophalangeal/metatarsophalangeal joint, is located between the cannon bone and the pastern bone. It’s a complex structure composed of bones, ligaments, tendons, and cartilage. The sesamoid bones, two small bones at the back of the fetlock, act like pulleys, increasing the leverage of the deep digital flexor tendon. This intricate design allows for flexibility and shock absorption, crucial for the horse’s athletic performance.
This joint is subject to tremendous stress, especially during high-impact activities like running and jumping. The ligaments, including the suspensory ligament and collateral ligaments, provide stability to the fetlock, preventing excessive movement and injury. The joint capsule, filled with synovial fluid, lubricates the joint and provides nourishment to the cartilage.
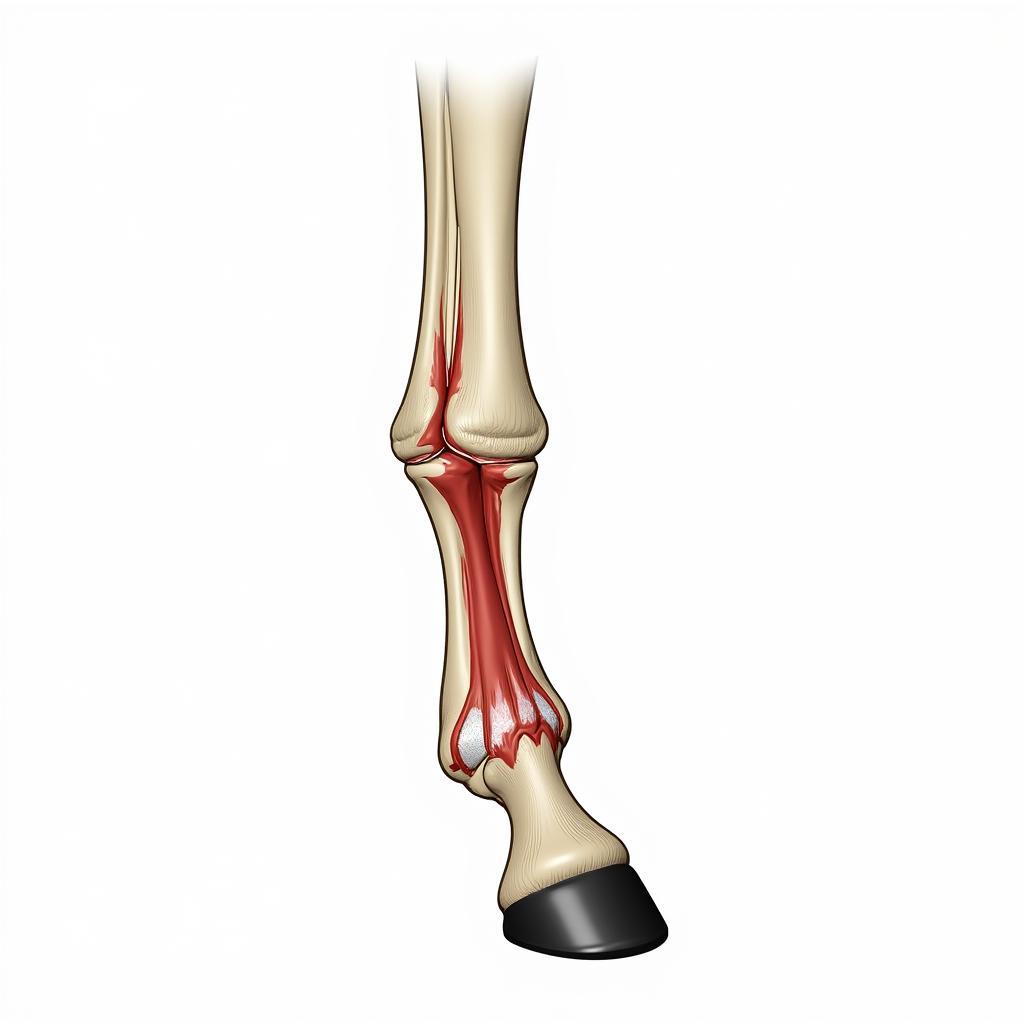 Horse Fetlock Anatomy Diagram
Horse Fetlock Anatomy Diagram
Common Fetlock Injuries in Horses
Due to the high stress placed on the fetlock, injuries to this area are relatively common. These can range from minor sprains and strains to more serious fractures and dislocations. Windpuffs, which are fluid-filled swellings around the fetlock, are a common sign of inflammation. More severe injuries, such as bowed tendons and suspensory ligament desmitis, can be career-ending for performance horses.
Understanding the signs of a fetlock injury is critical for early diagnosis and treatment. Lameness, swelling, heat, and pain on palpation are common indicators. If you suspect your horse has a fetlock injury, consult a veterinarian immediately. Early intervention is crucial for a successful recovery.
Protecting the Fetlock: The Importance of Horse Boots
Protecting the delicate fetlock joint is paramount, especially for horses involved in strenuous activities. Fetlock boots, also known as ankle boots, offer support and protection against impact and abrasion. These boots come in various designs and materials, each catering to specific disciplines and needs. Choosing the right boot is essential for optimal protection and comfort. If you are interested in purchasing fetlock boots, consider exploring our selection of fetlock horse boots. We also offer other protective boot options like cavallo boots for horses and quarter boots for horses.
Proper application of the boots is also crucial for their effectiveness. A poorly fitted or incorrectly applied boot can cause more harm than good. Learn how to put boots on a horse correctly to ensure optimal protection and prevent discomfort. Regularly check the boots for wear and tear and replace them when necessary.
What is the purpose of the fetlock?
The fetlock acts as a shock absorber, allowing the horse to move smoothly and efficiently.
What are the signs of a fetlock injury?
Lameness, swelling, heat, and pain are common signs of a fetlock injury.
How can I protect my horse’s fetlocks?
Using appropriate protective boots like fetlock boots can help protect your horse’s fetlocks.
Conclusion
The fetlock on a horse is a vital joint that requires careful attention and protection. Understanding its anatomy, recognizing potential injuries, and employing preventative measures are crucial for maintaining your horse’s health and soundness. By prioritizing fetlock care, you can contribute significantly to the longevity and well-being of your equine companion.
FAQ
- What is the main function of the fetlock joint? It acts as a shock absorber.
- What are the common types of fetlock injuries? Windpuffs, bowed tendons, and suspensory ligament desmitis.
- What are the signs of a fetlock injury in a horse? Lameness, swelling, and heat in the affected area.
- How can I prevent fetlock injuries in my horse? Use protective boots and proper training techniques.
- What type of boots are best for protecting the fetlock? Fetlock boots or ankle boots.
- When should I consult a veterinarian about a fetlock injury? As soon as you notice any signs of lameness or discomfort.
- Are there different types of fetlock boots available? Yes, there are various designs and materials available.
Need help with your horse? Contact us at Phone Number: 0772127271, Email: [email protected] Or visit us at QGM2+WX2, Vị Trung, Vị Thuỷ, Hậu Giang, Việt Nam. We have a 24/7 customer service team.