The horse, a majestic creature of power and grace, captivates us with its beauty and athleticism. But beneath its sleek exterior lies a complex and fascinating world of interconnected systems working tirelessly to support its every move. Understanding Horse Internal Anatomy is essential for any horse owner, not only to appreciate the intricacies of their equine partner but also to provide informed care, recognize potential health issues, and ensure their overall well-being.
A Journey Through the Equine Body: Exploring Key Systems
Let’s embark on a journey through the equine body, delving into the crucial systems that contribute to a horse’s overall health and functionality.
The Skeletal System: The Framework of Strength
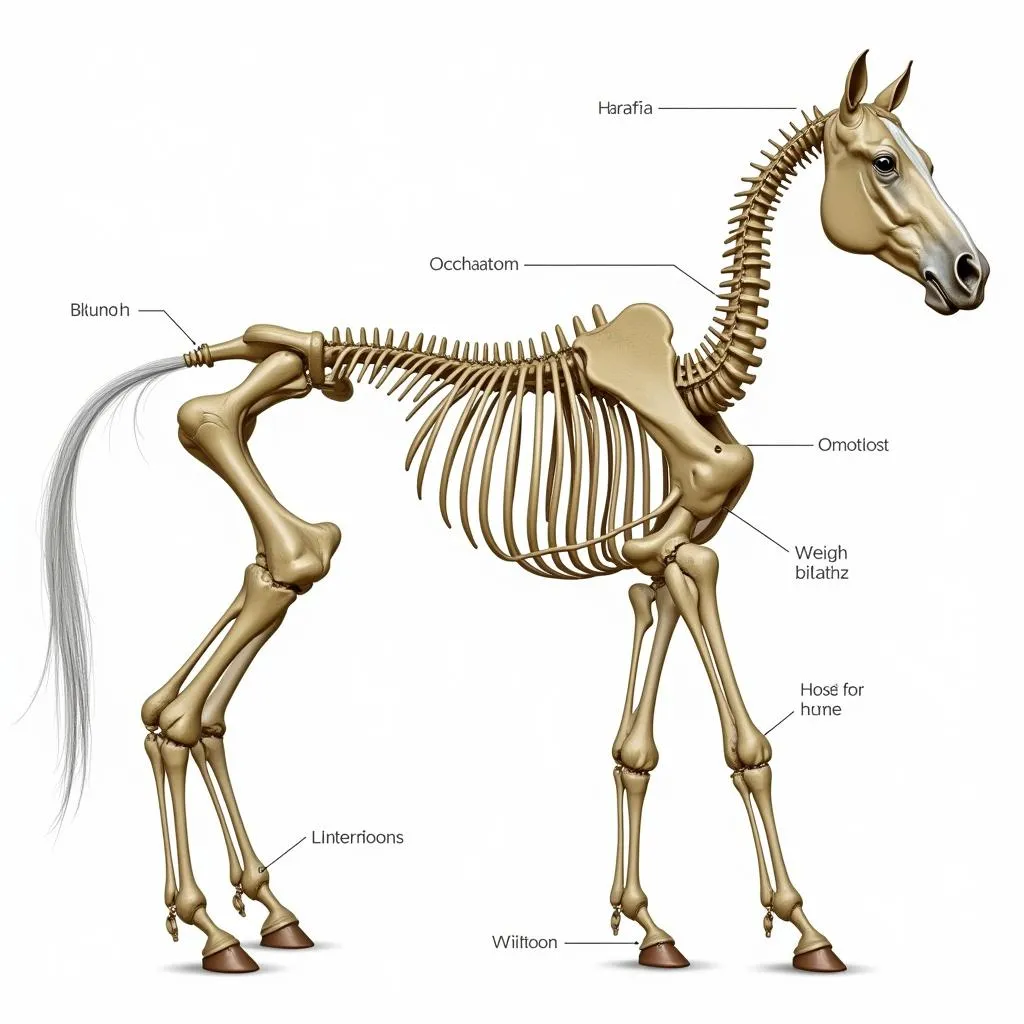 Detailed diagram of a horse skeleton
Detailed diagram of a horse skeleton
The skeletal system serves as the framework for the horse’s body, providing support, protection for vital organs, and leverage for movement. A horse’s skeleton comprises approximately 205 bones, categorized into two main sections: the axial skeleton (skull, vertebral column, ribs, sternum) and the appendicular skeleton (limbs).
A unique characteristic of the horse’s skeletal system is the absence of a collarbone. This adaptation allows for greater stride length and flexibility in the forelimbs, contributing to their impressive speed and agility. However, it also means the horse’s forelimbs are primarily supported by muscles, tendons, and ligaments, making them more susceptible to injuries.
The Muscular System: Powering Every Stride
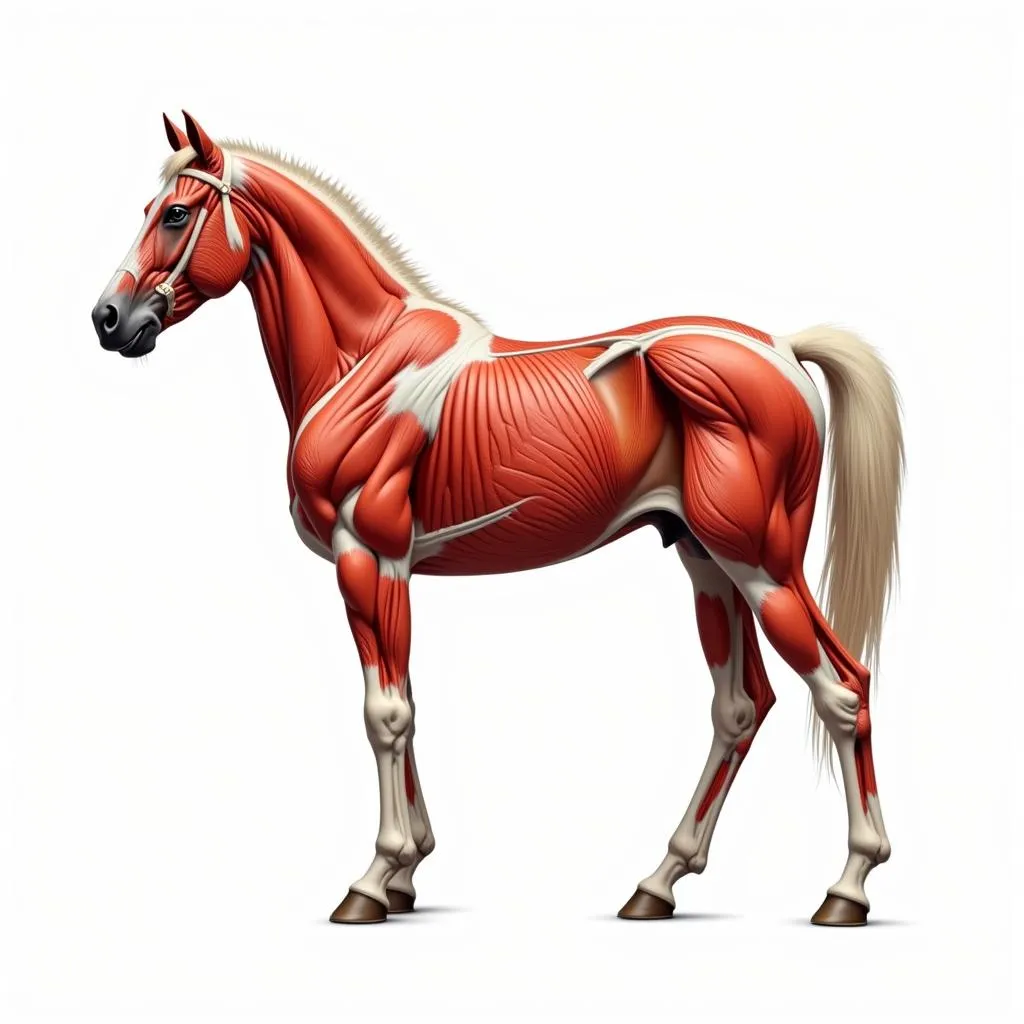 Horse muscles with labels for different groups
Horse muscles with labels for different groups
The muscular system, a complex network of over 700 muscles, is responsible for virtually every movement a horse makes. These muscles work in perfect coordination, contracting and relaxing to produce the power, agility, and grace that define the equine athlete.
Horses possess three types of muscle: skeletal muscle (responsible for voluntary movements), smooth muscle (found within internal organs and blood vessels), and cardiac muscle (found only in the heart).
Understanding the equine muscular system is crucial for recognizing signs of fatigue, strain, or injury. Proper conditioning, training, and warm-up routines are essential for maintaining muscle health and preventing potential problems.
The Digestive System: A Unique Herbivore Design
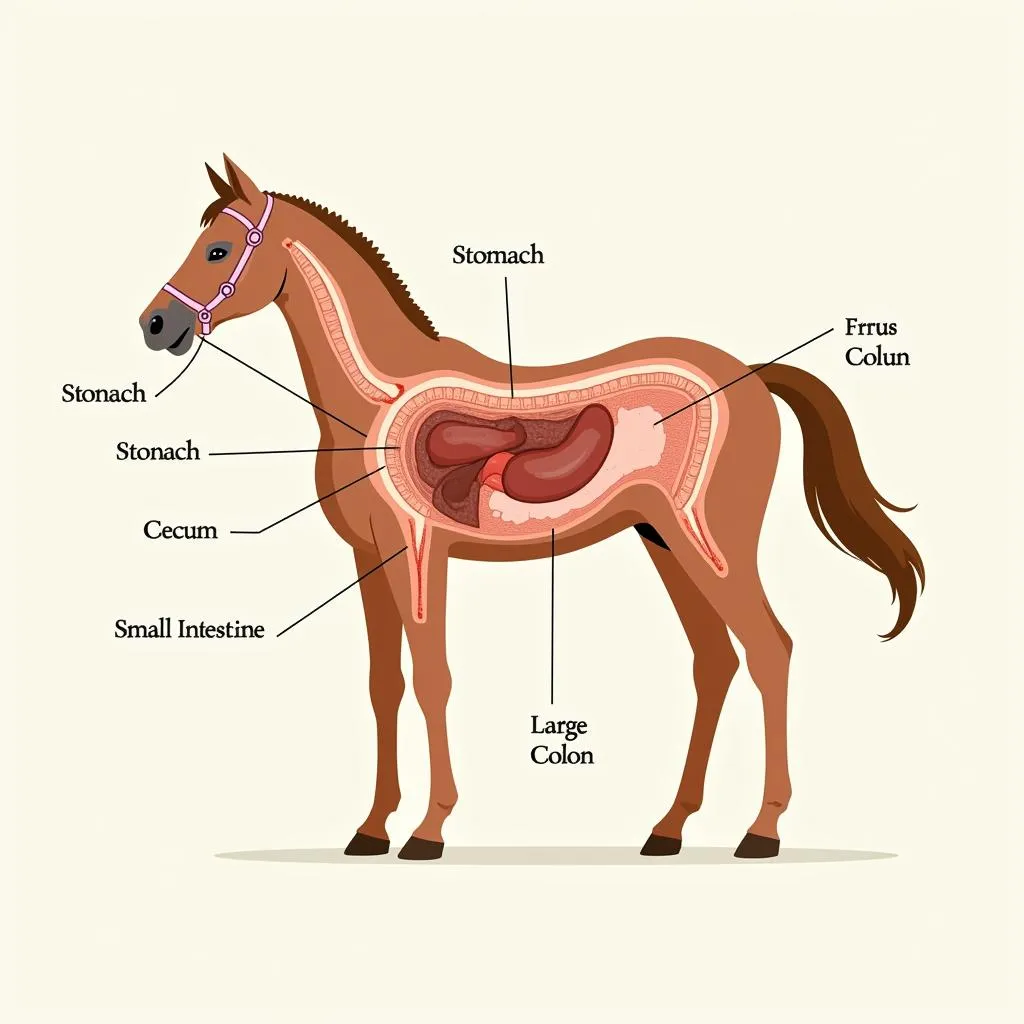 Cross-section illustration of a horse's digestive tract
Cross-section illustration of a horse's digestive tract
Horses are herbivores with a unique digestive system specifically adapted for breaking down plant material. Unlike ruminants with multiple stomachs, horses have a single stomach and rely heavily on their hindgut (cecum and large colon) for fermentation.
The horse’s digestive system is highly efficient at extracting nutrients from forage but also sensitive to changes in diet and routine. Sudden shifts in feed, stress, and other factors can disrupt the delicate balance of bacteria in the hindgut, leading to colic, a potentially life-threatening condition.
The Respiratory System: Fueling Athletic Performance
The respiratory system, comprised of the nostrils, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, and lungs, plays a critical role in delivering oxygen to the body and removing carbon dioxide. This system is particularly important in horses due to their athletic nature and high oxygen demands during exercise.
Understanding the normal respiratory rate and effort in horses is essential for recognizing signs of respiratory distress, which can indicate a variety of health issues.
Frequently Asked Questions about Horse Internal Anatomy
- What is the most common health problem related to horse internal anatomy? Colic, a digestive disorder, is one of the most common and potentially serious health issues affecting horses.
- Why is it important to understand the horse’s muscular system? Understanding the muscular system is crucial for recognizing signs of fatigue, strain, or injury, allowing for appropriate care and prevention of further issues.
- How does a horse’s diet affect its digestive health? As herbivores, horses thrive on a diet primarily consisting of forage. Sudden changes in feed can disrupt their sensitive digestive system, leading to colic and other health problems.
Exploring Further:
For more in-depth information on specific aspects of horse internal anatomy, explore our other articles on:
- Equine Skeletal Structure: [Link to article on horse skeletal system]
- The Equine Digestive System: [Link to article on horse digestive system]
- Maintaining Respiratory Health in Horses: [Link to article on horse respiratory health]
If you have any concerns about your horse’s health or need further assistance, our team at Justus Horses USA is here to help. Contact us at Phone Number: 0772127271, Email: [email protected], or visit us at QGM2+WX2, Vị Trung, Vị Thuỷ, Hậu Giang, Việt Nam. We offer 24/7 customer support to address all your equine needs.