The extensor tendon in a horse plays a crucial role in allowing the horse to move with power and grace. Located along the back of the leg, from the knee down to the hoof, this vital tendon is responsible for extending the leg and carrying the horse’s weight. Any injury to this tendon can significantly impact a horse’s performance and overall well-being.
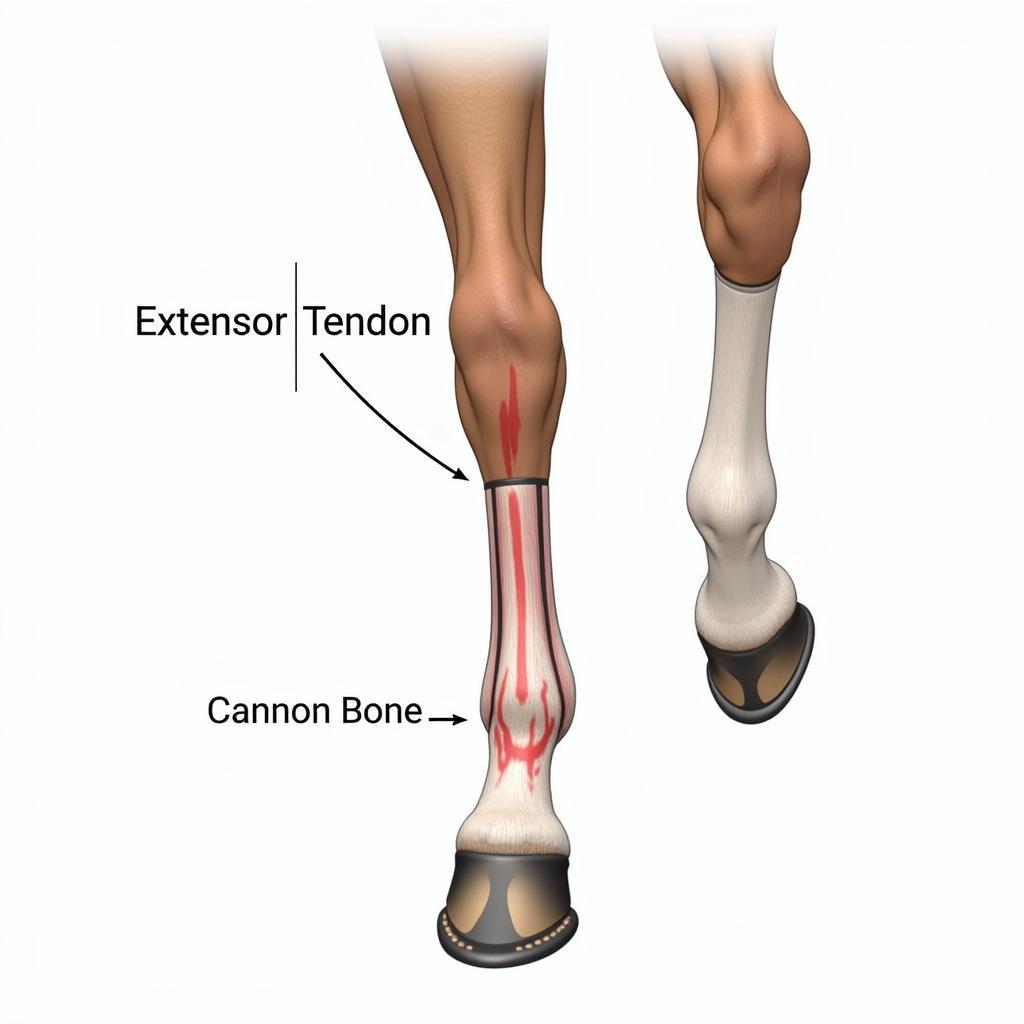 Equine Extensor Tendon Anatomy
Equine Extensor Tendon Anatomy
Common Causes of Extensor Tendon Injuries
Extensor tendon injuries, though less common than injuries to the flexor tendons, are a serious concern for horse owners. They often stem from:
- Trauma: A direct blow to the back of the leg, such as a kick from another horse or hitting a solid object, can cause damage to the tendon.
- Overstretching: Extreme overextension of the leg during activities like jumping, racing, or even slipping can overstress the extensor tendon, leading to injury.
- Poor Shoeing: Incorrect shoeing can alter the horse’s biomechanics, placing undue strain on the extensor tendon.
- Lacerations: Deep cuts or punctures to the back of the leg can sever or damage the extensor tendon.
Recognizing the Signs
Early detection is key in treating extensor tendon injuries effectively. Be vigilant for these signs:
- Lameness: The most obvious sign is often lameness, particularly when the horse is asked to put weight on the affected leg.
- Swelling: You might notice swelling along the back of the leg, directly over the tendon.
- Heat: The area around the injured tendon will likely feel warm to the touch.
- Pain: The horse may show signs of pain when the area is touched or manipulated.
- Dropping of the Toe: In more severe cases, the horse’s toe may drop due to the inability to extend the leg fully.
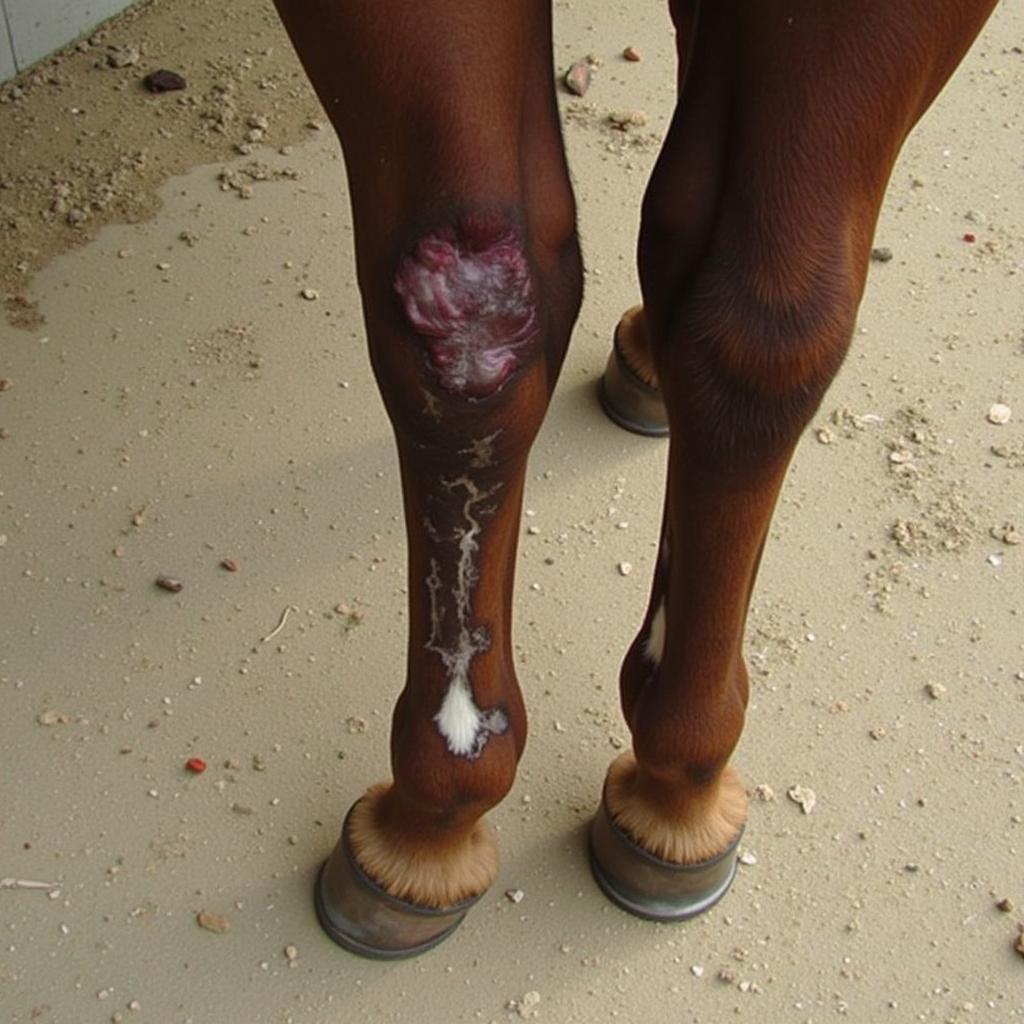 Swelling in Horse Leg Indicative of Extensor Tendon Injury
Swelling in Horse Leg Indicative of Extensor Tendon Injury
Diagnosis and Treatment
If you suspect your horse has an extensor tendon injury, immediate veterinary attention is crucial. A veterinarian will perform a thorough examination, which may include:
- Physical Exam: Palpating the tendon to assess heat, swelling, and pain response.
- Ultrasound: An ultrasound examination can reveal the extent of the damage to the tendon fibers.
- X-rays: While not used to directly visualize the tendon, x-rays can help rule out any associated bone injuries.
Treatment plans vary depending on the severity of the injury. Options may include:
- Rest: Strict stall rest is crucial in the initial stages of healing.
- Cold Therapy: Applying ice packs to the affected area helps reduce inflammation.
- Bandaging and Support: Bandages or support boots can help stabilize the leg and reduce strain on the tendon.
- Medications: Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like phenylbutazone can help manage pain and swelling.
- Regenerative Therapies: Techniques such as platelet-rich plasma (PRP) or stem cell therapy may be used to promote healing.
- Surgery: In severe cases, surgical intervention might be necessary to repair the damaged tendon.
Rehabilitation and Long-Term Management
Rehabilitation plays a vital role in restoring the horse’s soundness following an extensor tendon injury. Your veterinarian will design a tailored rehabilitation program that may involve:
- Controlled Exercise: Gradually increasing the horse’s exercise level, starting with walking and progressing to trotting and cantering, as the tendon heals.
- Physical Therapy: Modalities like therapeutic ultrasound, laser therapy, and massage can help promote healing and reduce scar tissue formation.
- Corrective Shoeing: Specialized shoeing can help support the healing tendon and prevent re-injury.
 Horse Undergoing Rehabilitation for Extensor Tendon Injury
Horse Undergoing Rehabilitation for Extensor Tendon Injury
Expert Insight: “Early intervention is absolutely key when it comes to extensor tendon injuries,” says Dr. Sarah Thompson, DVM, a leading equine veterinarian specializing in sports medicine. “Prompt diagnosis and treatment, followed by a carefully managed rehabilitation program, significantly increase the chances of a successful outcome.”
Preventing Future Injuries
While not all injuries are preventable, you can take steps to minimize the risk for your horse:
- Maintain a Safe Environment: Ensure your horse’s environment is free from hazards that could cause injury.
- Warm-up and Cool-down: Always warm up your horse properly before exercise and cool down afterward.
- Proper Shoeing: Schedule regular farrier appointments to maintain correct hoof balance and shoeing.
- Listen to Your Horse: Pay attention to any subtle signs of lameness or discomfort. Early detection can prevent minor issues from becoming major problems.
Conclusion
Understanding the mechanics, risks, and signs of extensor tendon injuries is essential for any horse owner. By being informed and proactive, you can play a vital role in safeguarding your horse’s health and well-being. Remember, early detection and intervention offer the best chance for a successful recovery.
Need support? Contact us 24/7 at Phone Number: 0772127271, Email: [email protected] or visit us at QGM2+WX2, Vị Trung, Vị Thuỷ, Hậu Giang, Việt Nam. We have a dedicated customer care team ready to assist you.