Understanding the Anatomy Of The Horse is crucial for any horse owner or enthusiast. Whether you’re a seasoned equestrian or just starting your journey with these magnificent animals, a deeper knowledge of their physical structure will enhance your ability to care for them, train them, and appreciate their athleticism. We’ll explore the intricacies of the equine anatomy, from the skeletal framework to the muscular system, providing you with valuable insights into the horse’s form and function.
The Skeletal Framework: The Foundation of the Horse’s Anatomy
The horse’s skeleton is a marvel of engineering, designed for both power and grace. Comprised of over 200 bones, it provides the structural support for the horse’s body, protects vital organs, and serves as the attachment point for muscles, enabling movement. The skull, a complex structure of bones fused together, houses and protects the brain and sensory organs. The vertebral column, running from the skull to the tail, provides flexibility and support for the back and neck. The ribs, attached to the thoracic vertebrae, form the rib cage, protecting the heart and lungs.
The pelvis, a large, basin-shaped bone structure, connects the hind limbs to the vertebral column and supports the abdominal organs. The limbs, designed for locomotion, are composed of a series of long bones connected by joints. Understanding the horse front leg anatomy is particularly important for recognizing potential lameness issues. The bones of the legs are incredibly strong, capable of withstanding the forces generated during running and jumping.
The Muscular System: Powering the Horse’s Movement
The horse’s muscular system, intricately interwoven with the skeletal system, is responsible for generating the power and movement that make these animals so captivating. With over 700 muscles, the horse’s musculature is a complex network of fibers that contract and relax to produce a wide range of movements, from subtle shifts in weight to powerful strides. The large muscle groups of the hindquarters, including the gluteal and hamstring muscles, provide the propulsive force for locomotion.
What muscles are responsible for a horse’s facial expressions? Many small, intricate muscles around the eyes, mouth, and ears allow for a surprising range of expressions. These subtle movements often communicate the horse’s emotional state and play a key role in their social interactions.
Dr. Emily Carter, DVM, specializing in equine sports medicine, emphasizes the importance of understanding the muscular system: “Recognizing the location and function of key muscle groups is essential for effective training and injury prevention. Proper conditioning and targeted exercises can strengthen specific muscles, enhancing performance and reducing the risk of injury.”
What are the Key Components of the Horse’s Digestive System?
The horse’s digestive system, adapted for a herbivorous diet, is a marvel of efficiency, allowing them to extract nutrients from fibrous plant material. The process begins in the mouth, where teeth grind the food, mixing it with saliva. The food then travels down the esophagus to the stomach, where it undergoes initial digestion.
The cheek horse plays a significant role in manipulating food within the mouth. From the stomach, partially digested food moves into the small intestine, where further enzymatic breakdown occurs. The small intestine absorbs nutrients, which are then transported throughout the body.
The horse sacrum plays a vital role in supporting the digestive organs within the abdominal cavity. The next stage of digestion takes place in the large intestine, comprised of the cecum, large colon, and small colon. The cecum and large colon house a vast population of microorganisms that ferment the fibrous material, breaking down cellulose and releasing volatile fatty acids, which the horse absorbs as a major energy source.
The Importance of the Horse’s Hooves
The horse’s hooves are remarkably complex structures that bear the entire weight of the animal. Composed of keratin, the same material that makes up human fingernails, the hoof is a multi-layered structure that provides protection, shock absorption, and traction. The outer layer, the hoof wall, is thick and hard, while the inner layers are softer and more elastic. The horse tail bone, or coccygeal vertebrae, while seemingly distant from the hooves, plays a role in balance and overall posture, indirectly influencing the forces exerted on the hooves.
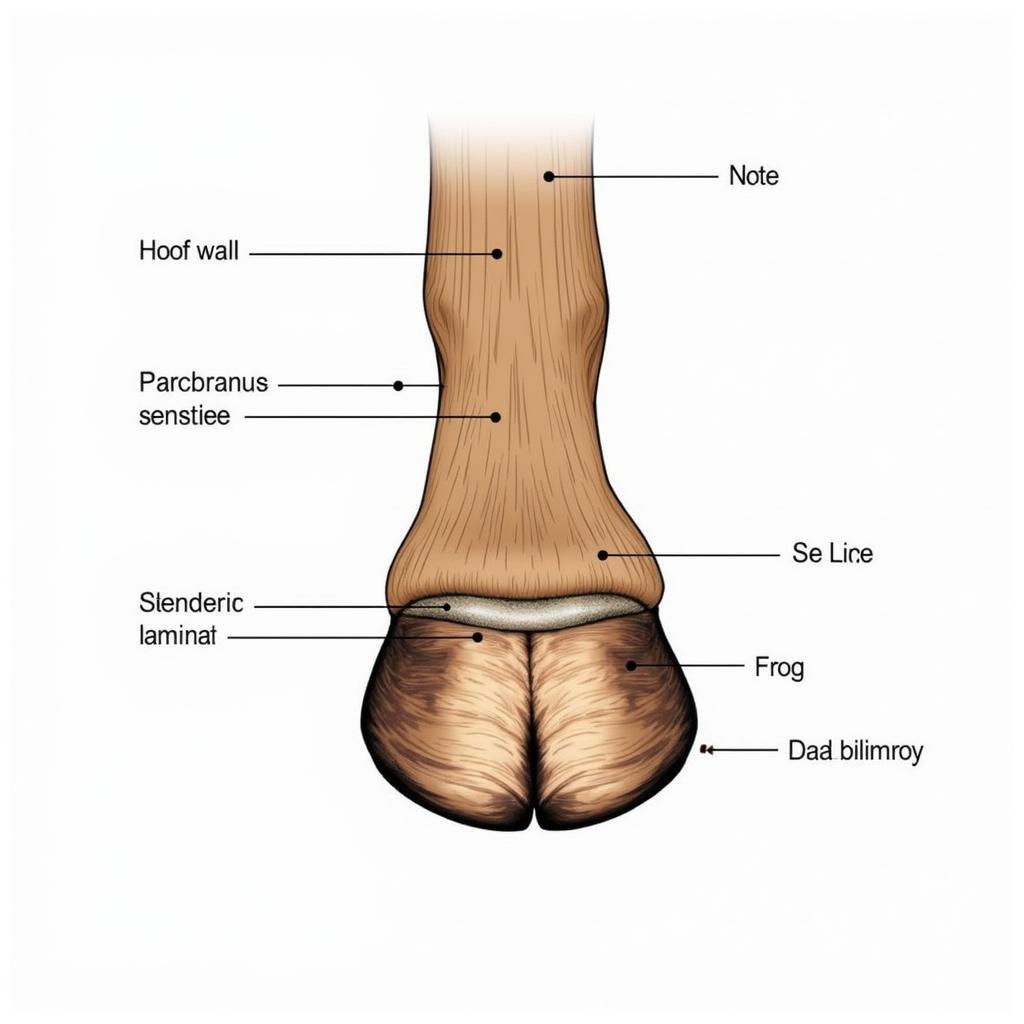 Horse Hoof Internal Structure
Horse Hoof Internal Structure
Proper hoof care is essential for maintaining the horse’s soundness and overall well-being. Regular trimming and shoeing, if necessary, are crucial for preventing imbalances and injuries. Leonardo da Vinci, a keen observer of equine anatomy, recognized the importance of the hoof, as evidenced in his studies of Leonardo’s horse. He meticulously documented the horse’s form and movement, including detailed drawings of the hooves.
Conclusion
Understanding the anatomy of the horse is a journey of discovery that enriches our appreciation for these remarkable animals. From the intricate skeletal framework to the powerful muscular system, each component plays a crucial role in the horse’s form and function. By delving into the intricacies of equine anatomy, we gain a deeper understanding of their physical capabilities, their health needs, and the wonders of their biological design.
FAQs
- How many bones are in a horse’s skeleton? (A horse’s skeleton has over 200 bones.)
- What is the purpose of the horse’s rib cage? (The rib cage protects the heart and lungs.)
- What is the largest muscle group in the horse? (The largest muscle group is in the hindquarters, responsible for propulsion.)
- What is the role of the cecum in the horse’s digestive system? (The cecum ferments fibrous material.)
- What material makes up the horse’s hooves? (Horse hooves are made of keratin.)
Need further assistance? Contact us at Phone Number: 0772127271, Email: [email protected] or visit us at QGM2+WX2, Vị Trung, Vị Thuỷ, Hậu Giang, Vietnam. We have a 24/7 customer support team.