The Horse Cell, a microscopic marvel, is the fundamental unit of life for our equine companions. Just like in all living organisms, these tiny structures work tirelessly to carry out all the functions necessary for a horse to thrive. From muscle contraction to energy production and even the flick of a tail, every action can be traced back to the intricate workings within each individual cell.
The Basics of a Horse Cell: Structure and Function
While seemingly simple at first glance, horse cells are anything but. They are complex factories buzzing with activity, each component playing a critical role. Let’s delve deeper into the key players:
1. Cell Membrane: Imagine a busy city with a secure border – that’s the cell membrane! It acts as a barrier, controlling what enters and exits the cell, ensuring a stable internal environment.
2. Cytoplasm: This jelly-like substance fills the cell, providing a platform for all the internal structures to interact and carry out their jobs. Think of it as the bustling city center where everything happens.
3. Nucleus: This is the cell’s control center, housing the horse’s genetic blueprint in the form of DNA. Just like a city hall holds important plans, the nucleus directs cell activities and determines hereditary traits.
4. Mitochondria: These powerhouses of the cell are responsible for producing energy through cellular respiration. They are like the city’s power plants, fueling all cellular activities.
5. Ribosomes: These tiny protein factories play a crucial role in building and repairing tissues within the horse’s body. Imagine them as construction crews, constantly working to maintain the city’s infrastructure.
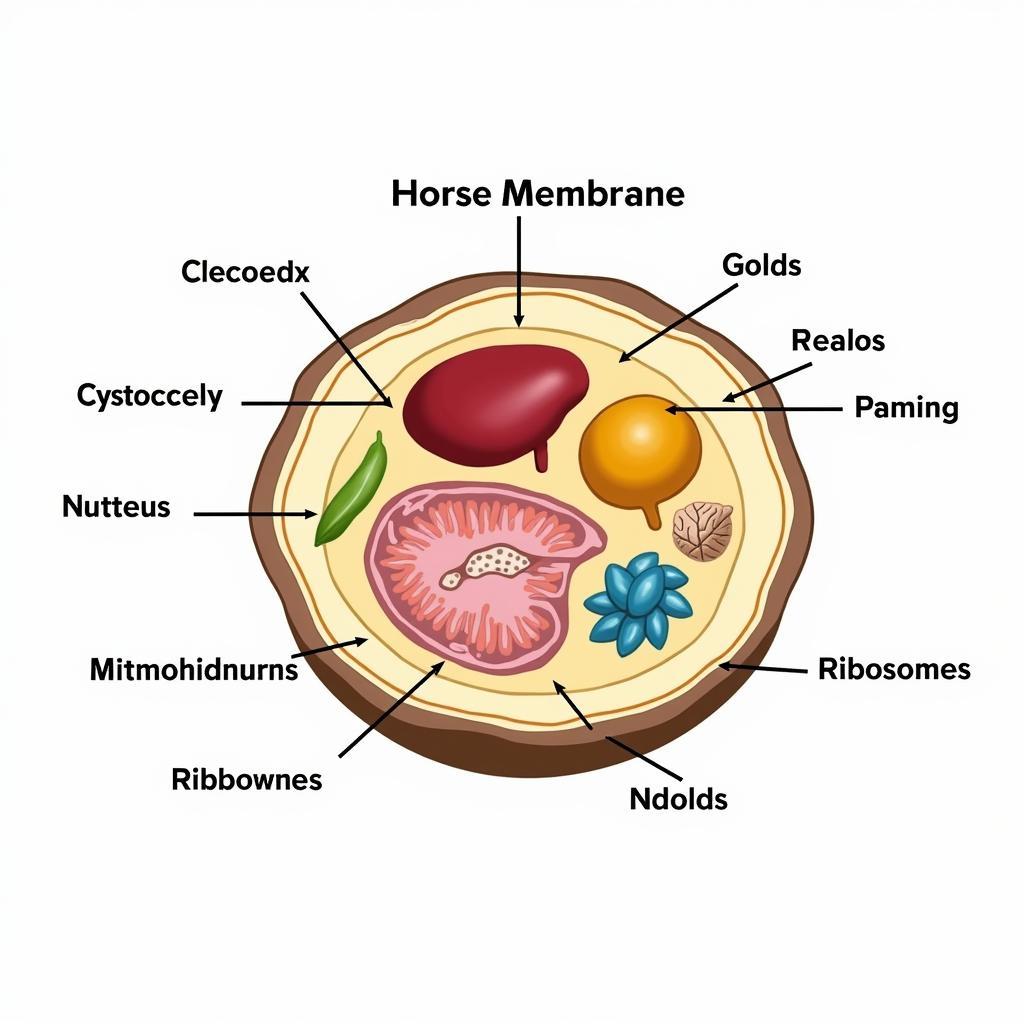 Horse Cell Structure
Horse Cell Structure
Specialized Horse Cells: A Symphony of Functions
Just as a city has specialized districts, the horse’s body is made up of different types of cells, each with unique structures and functions:
- Muscle Cells: These cells are the driving force behind every movement, from a gentle stroll to a powerful gallop. They contain specialized proteins that allow them to contract and relax, generating the force needed for locomotion.
- Nerve Cells: These cells are the communication specialists, transmitting signals throughout the body to coordinate every action. Imagine them as a complex network of wires, carrying messages between the brain and the rest of the horse’s body.
- Blood Cells: These cells are responsible for transporting oxygen, fighting infections, and aiding in healing. Just like a city’s delivery and emergency services, blood cells keep things running smoothly and respond quickly to any issues.
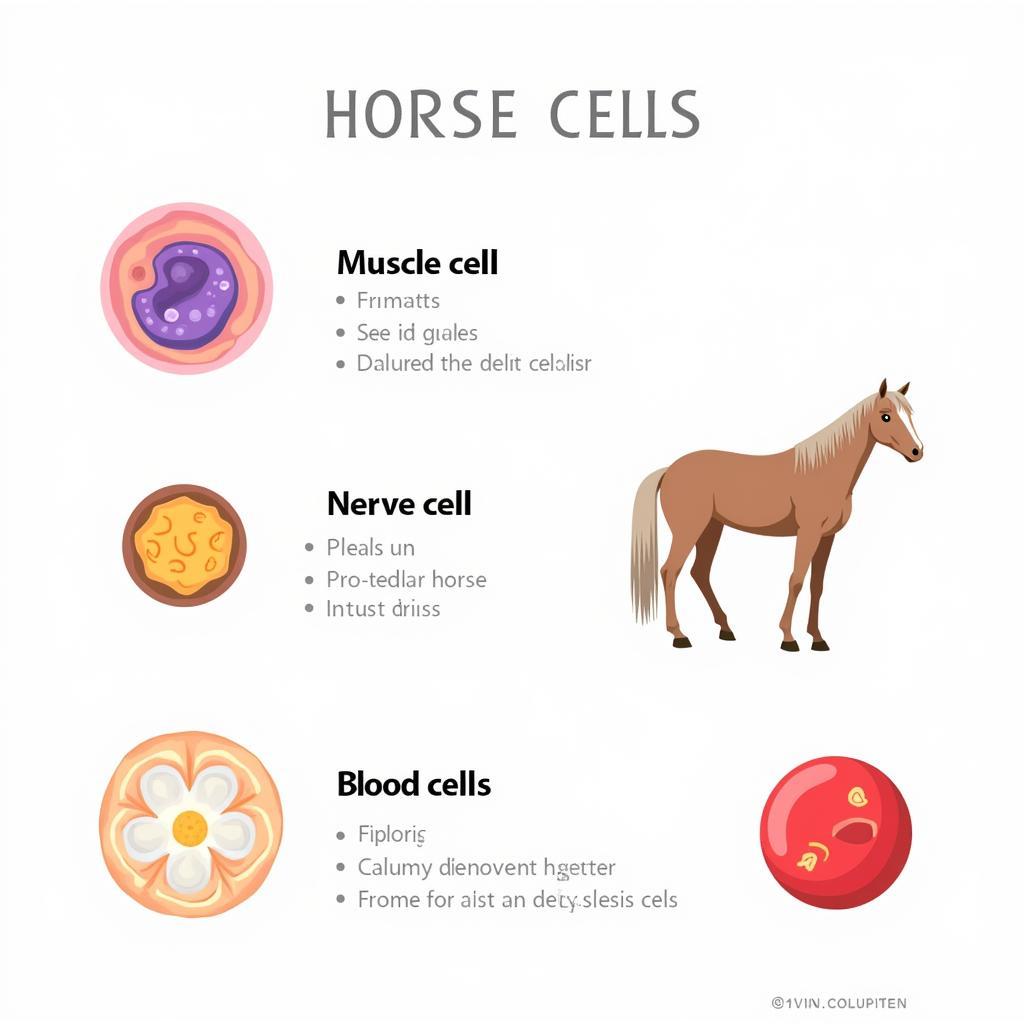 Specialized Horse Cells
Specialized Horse Cells
Horse Cell Health: The Foundation of Well-being
Just as a well-maintained city thrives, healthy cells are the cornerstone of a horse’s overall well-being. Several factors can impact cell health, including:
- Nutrition: Providing a balanced diet with all the essential nutrients is crucial for optimal cell function.
- Hydration: Water is essential for numerous cellular processes, so ensuring adequate water intake is vital.
- Exercise: Regular physical activity promotes blood flow and oxygen delivery to cells, supporting their health and function.
- Stress Management: Chronic stress can negatively impact cell health, so minimizing stressors is important.
Dr. Emily Carter, a leading equine veterinarian, emphasizes:
“Understanding the importance of horse cell health is fundamental to providing optimal care for our equine partners. By focusing on factors that support cellular well-being, we can help horses live longer, healthier lives.”
FAQs About Horse Cells
1. What is the most abundant type of cell in a horse’s body?
Red blood cells are the most numerous type of cell in a horse’s body, responsible for carrying oxygen throughout the bloodstream.
2. Can damaged horse cells be repaired?
Yes, the horse’s body has an incredible ability to repair and regenerate cells, especially with proper nutrition, rest, and veterinary care.
3. How do horse cells differ from other mammals?
While the basic structure of horse cells is similar to other mammals, there are subtle differences in size, shape, and function, reflecting the horse’s unique physiology and adaptations.
Exploring Further: The World of Horses
- To learn more about the Harford Horse Show Association, visit Harford Horse Show Association.
- Discover the excitement of horse auctions in Lumberton, NC, at Horse Auction in Lumberton NC.
 Healthy Horse, Healthy Cells
Healthy Horse, Healthy Cells
Maintaining Optimal Horse Cell Health: Key Takeaways
By understanding the crucial role of the horse cell, we can make informed decisions to support the well-being of our equine companions. From providing a balanced diet and ensuring proper hydration to promoting regular exercise and minimizing stress, every action contributes to maintaining the health of these tiny building blocks of life.
For any concerns regarding your horse’s health or for personalized advice on supporting their cellular well-being, don’t hesitate to contact our team of experts at Justus Horses USA.
Need Assistance?
Contact us:
Phone Number: 0772127271
Email: [email protected]
Address: QGM2+WX2, Vị Trung, Vị Thuỷ, Hậu Giang, Việt Nam
We have a dedicated customer support team available 24/7.